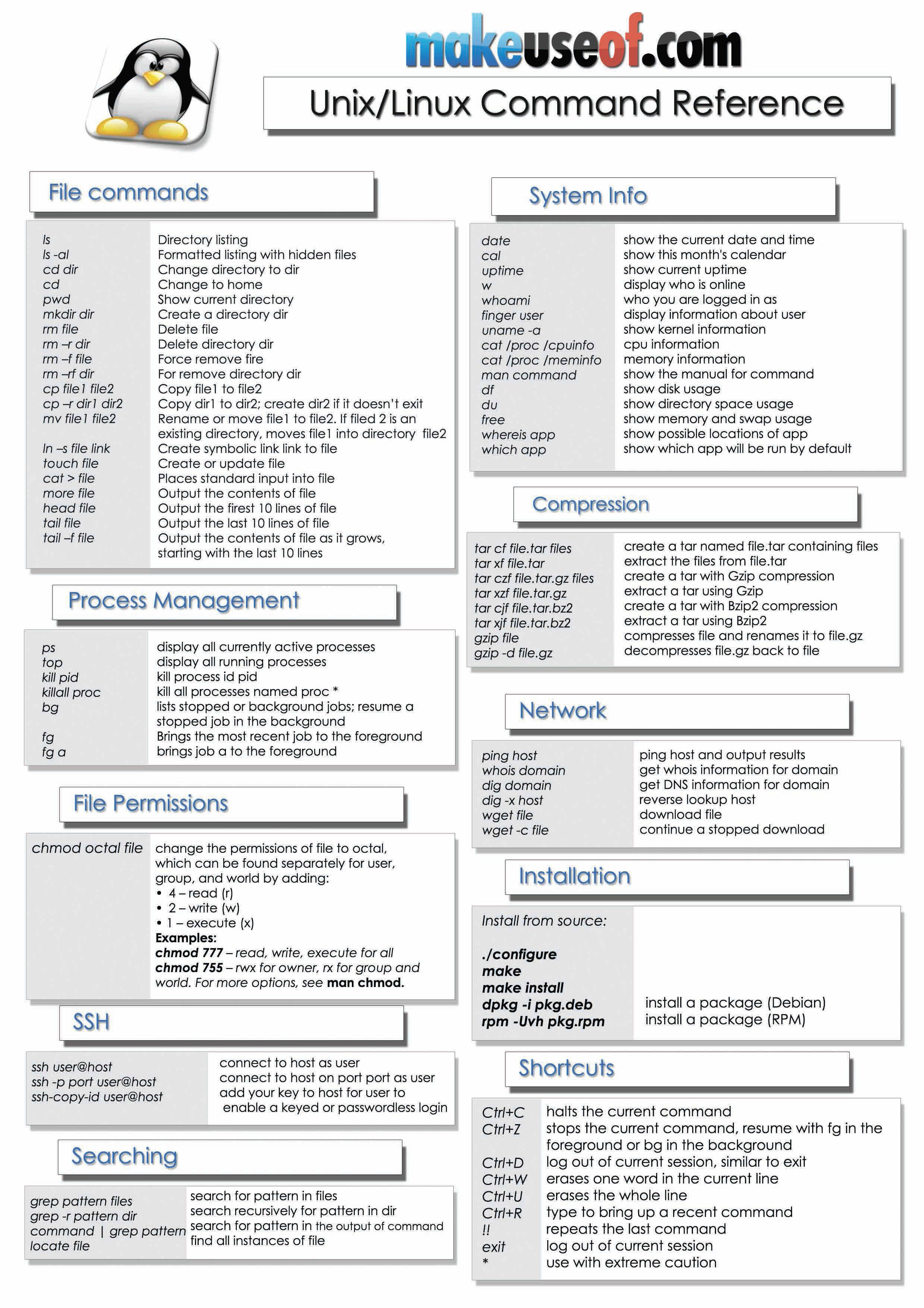
-
Redhat Format File System카테고리 없음 2020. 2. 29. 14:26
Multi-page HTML.Efficient file cloning, such as with the cp -reflink command.Per-file snapshotsThis functionality is also used by kernel subsystems such as Overlayfs and NFS for more efficient operation.Shared copy-on-write data extents are now enabled by default when creating an XFS file system, starting with the xfsprogs package version 4.17.0-2.el8.Note that Direct Access (DAX) devices currently do not support XFS with shared copy-on-write data extents. To create an XFS file system without this feature, use the following command:# mkfs.xfs -m reflink=0 block-deviceRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 can mount XFS file systems with shared copy-on-write data extents only in the read-only mode. 12.1.4. The /etc/sysconfig/nfs file and legacy NFS service names are no longer availableIn Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.0, the NFS configuration has moved from the /etc/sysconfig/nfs configuration file, which was used in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, to /etc/nfs.conf.The /etc/nfs.conf file uses a different syntax. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 attempts to automatically convert all options from /etc/sysconfig/nfs to /etc/nfs.conf when upgrading from Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.Both configuration files are supported in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat recommends that you use the new /etc/nfs.conf file to make NFS configuration in all versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux compatible with automated configuration systems.Additionally, the following NFS service aliases have been removed and replaced by their upstream names.
Redhat Format File System Linux
12.2.1. The BOOM boot manager simplifies the process of creating boot entriesBOOM is a boot manager for Linux systems that use boot loaders supporting the BootLoader Specification for boot entry configuration. It enables flexible boot configuration and simplifies the creation of new or modified boot entries: for example, to boot snapshot images of the system created using LVM.BOOM does not modify the existing boot loader configuration, and only inserts additional entries.
The existing configuration is maintained, and any distribution integration, such as kernel installation and update scripts, continue to function as before.BOOM has a simplified command-line interface (CLI) and API that ease the task of creating boot entries. 12.2.3. LUKS2 is now the default format for encrypting volumesIn RHEL 8, the LUKS version 2 (LUKS2) format replaces the legacy LUKS (LUKS1) format. The dm-crypt subsystem and the cryptsetup tool now uses LUKS2 as the default format for encrypted volumes.
LUKS2 provides encrypted volumes with metadata redundancy and auto-recovery in case of a partial metadata corruption event.Due to the internal flexible layout, LUKS2 is also an enabler of future features. It supports auto-unlocking through the generic kernel-keyring token built in libcryptsetup that allow users unlocking of LUKS2 volumes using a passphrase stored in the kernel-keyring retention service.Other notable enhancements include. 12.2.10. New overrides section of the DM Multipath configuration fileThe /etc/multipath.conf file now includes an overrides section that allows you to set a configuration value for all of your devices.
Linux File System
These attributes are used by DM Multipath for all devices unless they are overwritten by the attributes specified in the multipaths section of the /etc/multipath.conf file for paths that contain the device. This functionality replaces the alldevs parameter of the devices section of the configuration file, which is no longer supported. 12.2.11. NVMe/FC is fully supported on Broadcom Emulex and Marvell Qlogic Fibre Channel adaptersThe NVMe over Fibre Channel (NVMe/FC) transport type is now fully supported in Initiator mode when used with Broadcom Emulex and Marvell Qlogic Fibre Channel 32Gbit adapters that feature NVMe support.NVMe over Fibre Channel is an additional fabric transport type for the Nonvolatile Memory Express (NVMe) protocol, in addition to the Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) protocol that was previously introduced in Red Hat Enterprise Linux.Enabling NVMe/FC. 12.2.12. Support for Data Integrity Field/Data Integrity Extension (DIF/DIX)DIF/DIX is an addition to the SCSI Standard. It remains in Technology Preview for all HBAs and storage arrays, except for those specifically listed as supported.DIF/DIX increases the size of the commonly used 512 byte disk block from 512 to 520 bytes, adding the Data Integrity Field (DIF).
Xfs File System
The DIF stores a checksum value for the data block that is calculated by the Host Bus Adapter (HBA) when a write occurs. The storage device then confirms the checksum on receipt, and stores both the data and the checksum. Conversely, when a read occurs, the checksum can be verified by the storage device, and by the receiving HBA.